
USA

India

Turkey

Canada

Singapore

Your Intelligent medical assistant 24*7
Welcome to MediPocket, Where top care is beyond borders.
Hello I am Dr. AI, Your artificially Intelligent Healthcare companion.
Crafted by a brillliant teak of engineers, doctors, and scientists. I harness the power of LLM (Large Language Model) to connect with vast medical data.
Let me guide you seamlessly, from onboarding to navigating your health journey, ensuring you find the best option for your well being. Your health is simplified and personalized, Welcome to the future of medicine.
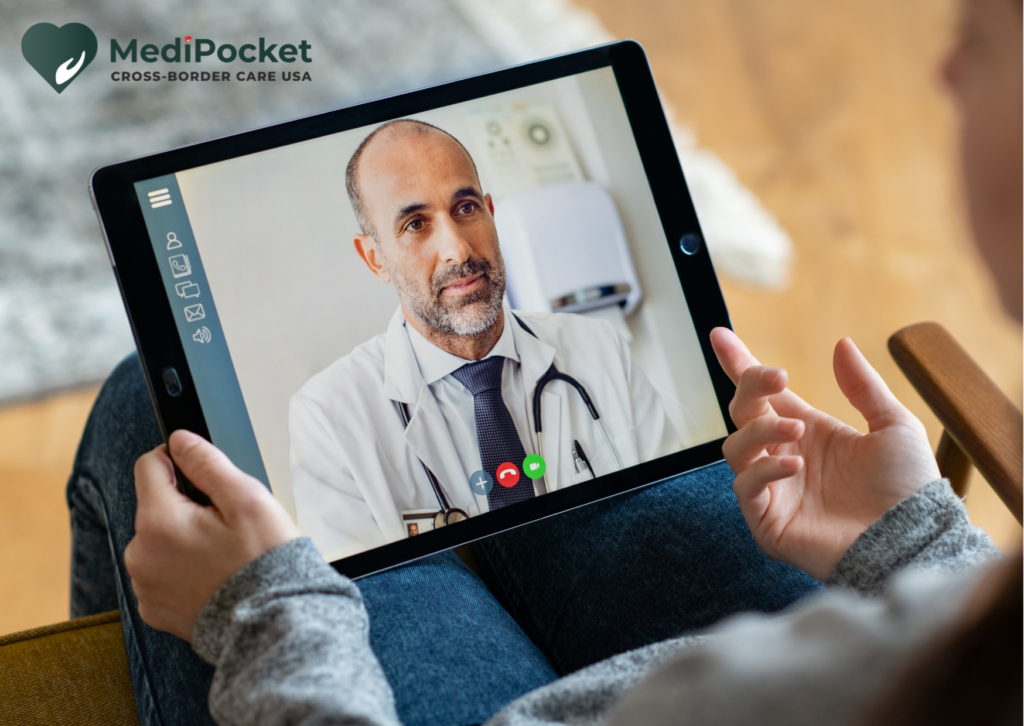


Second Opinion
Get the accessible and Premium Remote Second Opinion from the Best Hospitals in the USA.
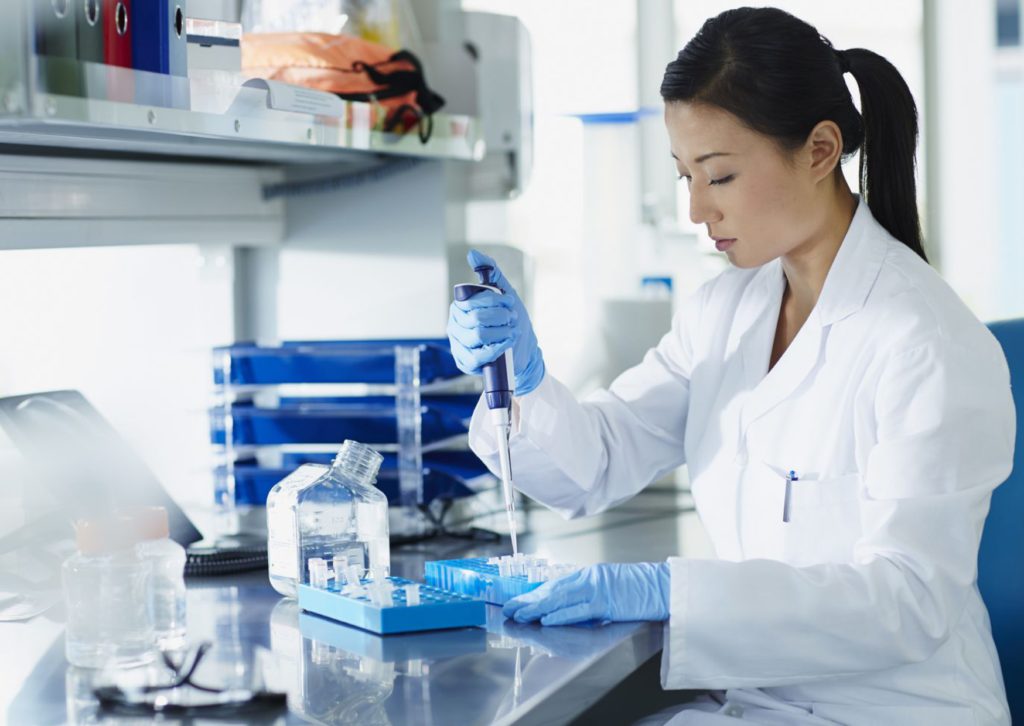

Clinical Trial
The Cutting-edge clinical Trials from the top hospitals in the US using the advance technology.

Treatment
Sustainable Treatment of the patients from the Expertized doctors in United States of America.
Get the accessible and Premium Remote Second Opinion from the Best Hospitals in the USA.
Global Lite
Starting at
$19/Month
Annual Benefits
Global Family
Starting at
$45/Month
Annual Benefits
USA Experts Second Opinion
Why?
When?
Clinical Trials in USA
Why?
When?

Dr.A.Eli Gabayan

Dr. Raj Kanodia

Dr. Sam Najmabadi

Dr. Charles Swerdlow

Dr. Lauren M. Freid

Dr. Filippo Pinto E Vairo
Knowledge is your key. Know about your healthcare and Second Opinion options


John
Cancer
USA

Preya PB
Second Opinion - PCOD, Gynecologists

USA


Bhavyashree
Treatment - Pediatric Nasal Reconstructive Plastic Surgery

India


Wife (want to keep private)
Second Opinion - Cardiologist

USA


Prateek
Second Opinion - Chronic Ear Issues, Pediatric

USA


Ms. S (want to be private)
Treatment - Nose job, Plastic Surgery

Canada


Dr. Debanjan
Second Opinion - Bronchiectasis, Pulmonologist

Turkey


Ibrahim M.
Treatment -Kidney Transplant, UCLA Hospital

Saudi Arabia


Second Opinion
Heart health, Cardiologists

Singapore


Dr. Amina Khan
Cardiothoracic Surgeon

India


Dr. Amina Khan
Cardiothoracic Surgeon

India


Dr. Juan Carlos Ramirez
Oncologist

Canada


John
Cancer
USA

Preya PB
Second Opinion - PCOD, Gynecologists

USA


Bhavyashree
Treatment - Pediatric Nasal Reconstructive Plastic Surgery

India


Wife (want to keep private)
Second Opinion - Cardiologist

USA


Prateek
Second Opinion - Chronic Ear Issues, Pediatric

USA


Ms. S (want to be private)
Treatment - Nose job, Plastic Surgery

Canada


Dr. Debanjan
Second Opinion - Bronchiectasis, Pulmonologist

Turkey


Pediatric Cancer: Overview and Treatment

Kate Middleton Cancer Diagnosis
Stomach Cancer and How to Cure it?

Pediatric Cancer: Overview and Treatment

Kate Middleton Cancer Diagnosis



